Logical Operators
Logical operations work with Boolean expressions to yield an answer for expressions. Individually they are quite straightforward but can be combined to create complex expressions.
And Operator
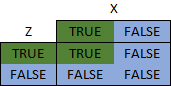
The And operator requires 2 Boolean values, gives a True answer when both sides of the argument are also True, otherwise False. A logic table demonstrates this more clearly.
|
For the expression: Z And X
|
 |
|
Sub andOperator() Dim X As Boolean, Z As Boolean X = True: Z = True: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " and " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X And Z) X = True: Z = False: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " and " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X And Z) X = False: Z = True: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " and " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X And Z) X = False: Z = False: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " and " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X And Z) End Sub
Running the code above produces this result in the immediate window:
| True and True evaluate to True True and False evaluate to False False and True evaluate to False False and False evaluate to False |
Or Operator
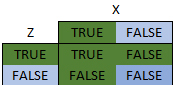
The Or operator requires 2 Boolean values, gives a value of True when either side of the argument is True. A logic table demonstrates this more clearly.
|
For the expression: Z Or X
|
 |
|
Sub orOperator() Dim X As Boolean, Z As Boolean X = True: Z = True: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " or " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X Or Z) X = True: Z = False: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " or " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X Or Z) X = False: Z = True: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " or " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X Or Z) X = False: Z = False: Debug.Print CStr(X) & " or " & CStr(Z) & " evaluate to " & CStr(X Or Z) End Sub
Running the code above produces this result in the immediate window:
| True or True evaluate to True True or False evaluate to True False or True evaluate to True False or False evaluate to False |
Not Operator
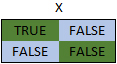
The Not operator requires 1 Boolean value, gives a value of True when the argument is False, and False when the argument is True. A logic table demonstrates this more clearly.
|
For the expression: Not X
|
 |
|
Sub notOperator() Dim X As Boolean X = True: Debug.Print "Not " & CStr(X) & " evaluates to " & CStr(Not X) X = False: Debug.Print "Not " & CStr(X) & " evaluates to " & CStr(Not X) End Sub
Running the code above produces this result in the immediate window:
| Not True evaluates to False Not False evaluates to True |
A Slightly More Practical Example
Public Sub testOperator() Dim x As Integer Dim y As Integer Dim z As Boolean x = 1 y = 2 z = False 'And operator If (x = 1) And (y = 1) Then Debug.Print "The AND expression has evaluated to true!" Else Debug.Print "The AND expression has evaluated to false!" End If 'Or operator If (x = 1) Or (y = 1) Then Debug.Print "The OR expression has evaluated to true!" Else Debug.Print "The OR expression has evaluated to false!" End If 'Not operator If Not z Then 'z = false so Not z evaluates to true!!! Debug.Print "The NOT expression has evaluated to true!" Else Debug.Print "The NOT expression has evaluated to false!" End If End Sub
Running the code above produces this result in the immediate window:
|
The AND expression has evaluated to false! The OR expression has evaluated to true! The NOT expression has evaluated to true! |
Related Posts
Artithmetic Operators OperatorsUsing The Like Operator In Queries Operators